Understanding the forecaster parameters¶
Understanding what can be done when initializing a forecaster with skforecast can have a significant impact on the accuracy and effectiveness of the model. This guide highlights key considerations to keep in mind when initializing a forecaster and how these functionalities can be used to create more powerful and accurate forecasting models in Python.
We will explore the arguments that can be included in a ForecasterRecursive, but this can be extrapolated to any of the skforecast forecasters.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = None,
lags = None,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
differentiation = None,
fit_kwargs = None,
binner_kwargs = None,
forecaster_id = None
)
Tip
To be able to create and train a forecaster, at least regressor and lags and/or window_features must be specified.
General parameters¶
Regressor¶
Skforecast is a Python library that facilitates using scikit-learn regressors as multi-step forecasters and also works with any regressor compatible with the scikit-learn API. Therefore, any of these regressors can be used to create a forecaster:
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = None
)
Lags¶
To apply machine learning models to forecasting problems, the time series needs to be transformed into a matrix where each value is associated with a specific time window (known as lags) that precedes it. In the context of time series, a lag with respect to a time step t is defined as the value of the series at previous time steps. For instance, lag 1 represents the value at time step t-1, while lag m represents the value at time step t-m.
Learn more about machine learning for forecasting.
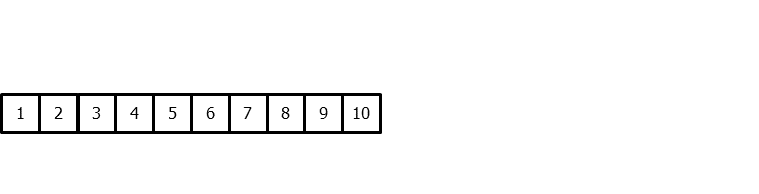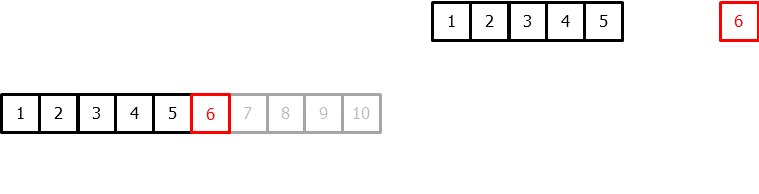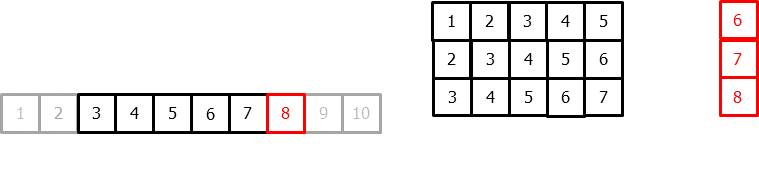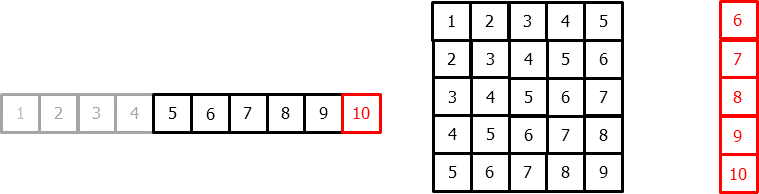
Time series transformation into a matrix of 5 lags and a vector with the value of the series that follows each row of the matrix.
# Create a forecaster using 5 lags
# ==============================================================================
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = 5
)
Window Features¶
When forecasting time series data, it may be useful to consider additional characteristics beyond just the lagged values. For example, the moving average of the previous n values may help to capture the trend in the series. The window_features argument allows the inclusion of additional predictors created with the previous values of the series.
More information: Window and custom features.
# Create a forecaster with window features
# ==============================================================================
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.preprocessing import RollingFeatures
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
window_features = RollingFeatures(
stats = ['mean', 'mean', 'min', 'max'],
window_sizes = [20, 10, 10, 10]
)
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = 5,
window_features = window_features
)
Transformers¶
Skforecast has two arguments in all the forecasters that allow more detailed control over input data transformations. This feature is particularly useful as many machine learning models require specific data pre-processing transformations. For example, linear models may benefit from features being scaled, or categorical features being transformed into numerical values.
Both arguments expect an instance of a transformer (preprocessor) compatible with the scikit-learn preprocessing API with the methods: fit, transform, fit_transform and, inverse_transform.
More information: Scikit-learn transformers and pipelines.
Example
In this example, a scikit-learn StandardScaler preprocessor is used for both the time series and the exogenous variables.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = StandardScaler(),
transformer_exog = StandardScaler()
)
Custom weights¶
The weight_func parameter allows the user to define custom weights for each observation in the time series. These custom weights can be used to assign different levels of importance to different time periods. For example, assign higher weights to recent data points and lower weights to older data points to emphasize the importance of recent observations in the forecast model.
More information: Weighted time series forecasting.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
# Custom function to create weights
# ==============================================================================
def custom_weights(index):
"""
Return 0 if index is between 2012-06-01 and 2012-10-21.
"""
weights = np.where(
(index >= '2012-06-01') & (index <= '2012-10-21'),
0,
1
)
return weights
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = custom_weights
)
Differentiation¶
Time series differentiation involves computing the differences between consecutive observations in the time series. When it comes to training forecasting models, differentiation offers the advantage of focusing on relative rates of change rather than directly attempting to model the absolute values. Skforecast, version 0.10.0 or higher, introduces a novel differentiation parameter within its Forecasters.
More information: Time series differentiation.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
differentiation = 1
)
Inclusion of kwargs in the regressor fit method¶
Some regressors include the possibility to add some additional configuration during the fitting method. The predictor parameter fit_kwargs allows these arguments to be set when the forecaster is declared.
Danger
To add weights to the forecaster, it must be done through the weight_func argument and not through a fit_kwargs.
Example
The following example demonstrates the inclusion of categorical features in an LGBM regressor. This must be done during the LGBMRegressor fit method. Fit parameters lightgbm
More information: [Categorical features]../user_guides/categorical-features.html#native-implementation-for-categorical-features).
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(),
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
differentiation = None,
fit_kwargs = {'categorical_feature': ['exog_1', 'exog_2']}
)
Intervals conditioned on predicted values (binned residuals)¶
When creating prediction intervals, skforecast uses a QuantileBinner class to bin data into quantile-based bins using numpy.percentile. This class is similar to KBinsDiscretizer but faster for binning data into quantile-based bins. Bin intervals are defined following the convention: bins[i-1] <= x < bins[i].
More information: Intervals conditioned on predicted values (binned residuals).
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(),
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
differentiation = None,
fit_kwargs = None,
binner_kwargs = {'n_bins': 10}
)
Forecaster ID¶
Name used as an identifier of the forecaster. It may be used, for example to identify the time series being modeled.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.recursive import ForecasterRecursive
forecaster = ForecasterRecursive(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
differentiation = None,
fit_kwargs = None,
binner_kwargs = None,
forecaster_id = 'my_forecaster'
)
Direct multi-step parameters¶
For the Forecasters that follow a direct multi-step strategy (ForecasterDirect and ForecasterDirectMultiVariate), there are two additional parameters in addition to those mentioned above.
Steps¶
Direct multi-step forecasting consists of training a different model for each step of the forecast horizon. For example, to predict the next 5 values of a time series, 5 different models are trained, one for each step. As a result, the predictions are independent of each other.
The number of models to be trained is specified by the steps parameter.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.direct import ForecasterDirect
forecaster = ForecasterDirect(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
steps = 5,
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
fit_kwargs = None,
forecaster_id = 'my_forecaster'
)
Number of jobs¶
The n_jobs parameter allows multi-process parallelization to train regressors for all steps simultaneously.
The benefits of parallelization depend on several factors, including the regressor used, the number of fits to be performed, and the volume of data involved. When the n_jobs parameter is set to 'auto', the level of parallelization is automatically selected based on heuristic rules that aim to choose the best option for each scenario.
For a more detailed look at parallelization, visit Parallelization in skforecast.
# Create a forecaster
# ==============================================================================
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from skforecast.direct import ForecasterDirect
forecaster = ForecasterDirect(
regressor = LGBMRegressor(random_state=123, verbose=-1),
steps = 5,
lags = 5,
window_features = None,
transformer_y = None,
transformer_exog = None,
weight_func = None,
fit_kwargs = None,
n_jobs = 'auto',
forecaster_id = 'my_forecaster'
)