Recursive multi-step forecasting
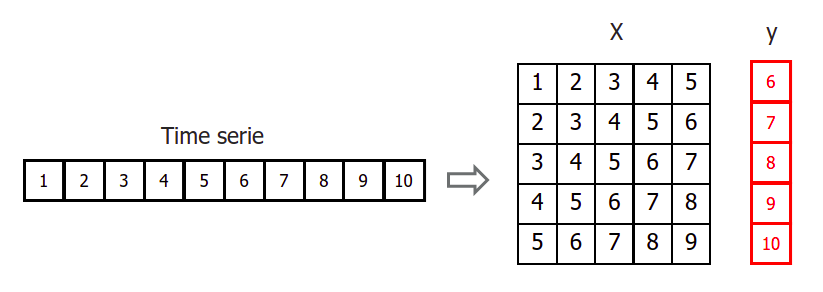
Since the value of t(n) is required to predict the point t(n-1) , and t(n-1) is unknown, it is necessary to make recursive predictions in which, each new prediction, is based on the previous one. This process is known as recursive forecasting or recursive multi-step forecasting.
The main challenge when using machine learning models for recursive multi-step forecasting is transforming the time series in an matrix where, each value of the series, is related to the time window (lags) that precedes it. This forecasting strategy can be easily generated with the classes ForecasterAutoreg and ForecasterAutoregCustom.
Libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skforecast.ForecasterAutoreg import ForecasterAutoreg
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
Data
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 url = ( 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JoaquinAmatRodrigo/skforecast/master/data/h2o.csv' )
data = pd . read_csv ( url , sep = ',' , header = 0 , names = [ 'y' , 'datetime' ])
data [ 'datetime' ] = pd . to_datetime ( data [ 'datetime' ], format = '%Y/%m/ %d ' )
data = data . set_index ( 'datetime' )
data = data . asfreq ( 'MS' )
data = data [ 'y' ]
data = data . sort_index ()
steps = 36
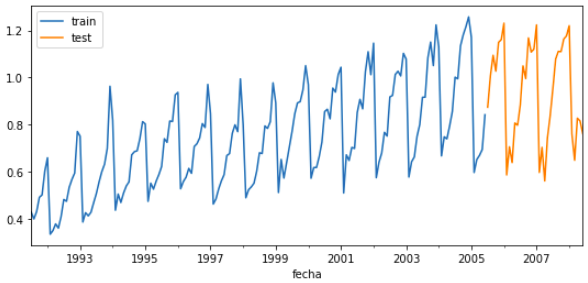
data_train = data [: - steps ]
data_test = data [ - steps :]
fig , ax = plt . subplots ( figsize = ( 9 , 4 ))
data_train . plot ( ax = ax , label = 'train' )
data_test . plot ( ax = ax , label = 'test' )
ax . legend ()
Create and train forecaster
forecaster = ForecasterAutoreg (
regressor = RandomForestRegressor ( random_state = 123 ),
lags = 15
)
forecaster . fit ( y = data_train )
forecaster
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 =================
ForecasterAutoreg
=================
Regressor: RandomForestRegressor(random_state=123)
Lags: [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15]
Window size: 15
Included exogenous: False
Type of exogenous variable: None
Exogenous variables names: None
Training range: [Timestamp('1991-07-01 00:00:00'), Timestamp('2005-06-01 00:00:00')]
Training index type: DatetimeIndex
Training index frequency: MS
Regressor parameters: {'bootstrap': True, 'ccp_alpha': 0.0, 'criterion': 'squared_error', 'max_depth': None, 'max_features': 'auto', 'max_leaf_nodes': None, 'max_samples': None, 'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0, 'min_samples_leaf': 1, 'min_samples_split': 2, 'min_weight_fraction_leaf': 0.0, 'n_estimators': 100, 'n_jobs': None, 'oob_score': False, 'random_state': 123, 'verbose': 0, 'warm_start': False}
Creation date: 2022-01-02 16:14:39
Last fit date: 2022-01-02 16:14:39
Skforecast version: 0.4.2
Prediction
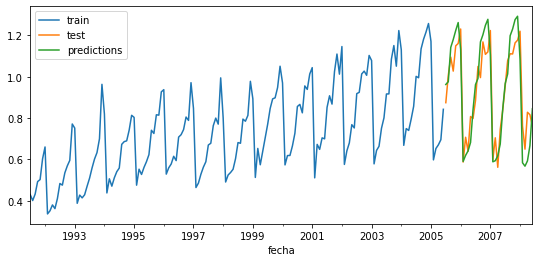
predictions = forecaster . predict ( steps = 36 )
predictions . head ( 3 )
2005-07-01 0.921840
2005-08-01 0.954921
2005-09-01 1.101716
Freq: MS, Name: pred, dtype: float64
fig , ax = plt . subplots ( figsize = ( 9 , 4 ))
data_train . plot ( ax = ax , label = 'train' )
data_test . plot ( ax = ax , label = 'test' )
predictions . plot ( ax = ax , label = 'predictions' )
ax . legend ()
error_mse = mean_squared_error (
y_true = data_test ,
y_pred = predictions
)
print ( f "Test error (mse): { error_mse } " )
Test error (mse): 0.00429855684785846
Feature importance
forecaster . get_feature_importance ()
feature
importance
lag_1
0.0123397
lag_2
0.0851603
lag_3
0.0134071
lag_4
0.00437446
lag_5
0.00318805
lag_6
0.00343593
lag_7
0.00313612
lag_8
0.00714094
lag_9
0.00783053
lag_10
0.0127507
lag_11
0.00901919
lag_12
0.807098
lag_13
0.00481128
lag_14
0.0163282
lag_15
0.0099792